By Kim Ross, DCN, CNS, LDN, IFMCP+
Fueling Focus: Optimizing Acetylcholine for Sharper Attention and Cognitive Performance
Table of Contents:
Introduction
Did you know?
- 1 in 25 adults have difficulty maintaining attention and focus.1
- Nearly half of individuals feel their attention span isn't what it used to be.2
Attention and cognitive performance are fundamental to daily functioning, influencing productivity, learning and decision-making. Unfortunately, focus-related difficulties are increasingly prevalent, affecting individuals across all age groups leading to an upward trend in adults seeking support to improve their focus and concentration. The growing prevalence of digital distractions, stress and inadequate nutrition exacerbates attention-related challenges.
This blog highlights the role of the cholinergic system and acetylcholine optimization in enhancing cognitive performance and sustaining mental clarity through integrative strategies, including nutrition, lifestyle factors and targeted nutrient support.
Acetylcholine and the Cholinergic System
The cholinergic system is a complex system involved in various peripheral and central nervous functions. Its most significant roles include:3,4
1) The transmission of signals across nerve cells for muscle activation, memory, learning, neuronal signaling, synaptic plasticity and sensory processing.
2) The synthesis and release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh).
Acetylcholine is a primary neurotransmitter that, as the name implies, is synthesized from acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) and choline. This neurotransmitter is essential for memory formation, learning and sustained attention. It acts at both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors throughout the brain, particularly in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, which are critical for executive function and memory recall.4 ACh is broken down into acetate and choline. Choline can then be recycled for use by nerves or can be converted back to phosphatidylcholine, a major component of cellular membranes.3,4
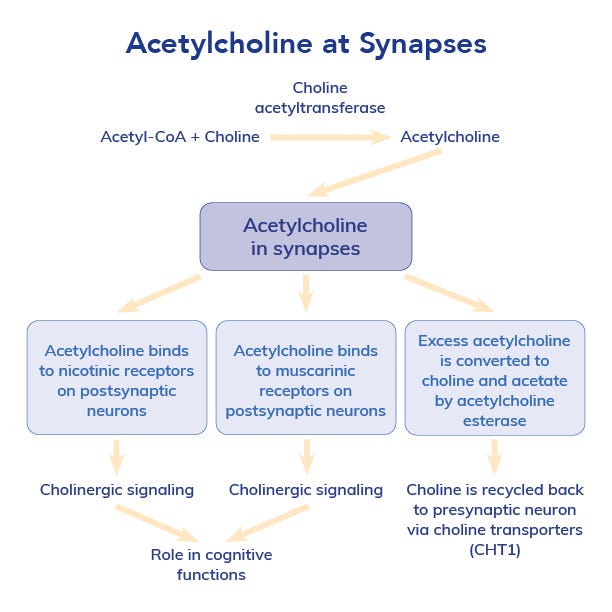

Studies show that individuals with higher acetylcholine activity demonstrate superior cognitive flexibility, faster reaction times and enhanced working memory. 5–7 Conversely, acetylcholine depletion is associated with reduced attention span, slower cognitive processing and impaired recall ability.8




Nutrition and Lifestyle Interventions for Acetylcholine Optimization
Several factors can influence acetylcholine levels, including poor dietary intake of choline, lack of physical activity and chronic stress. Given acetylcholine's role in cognitive performance, strategic interventions aimed at preserving and enhancing cholinergic function should be a focus of clinical care.
Nutrition
Consuming foods high in choline is crucial since this nutrient is needed to synthesize acetylcholine.
Key dietary sources include:
- Egg yolks (one of the highest sources of dietary choline)
- Beef and chicken liver
- Fish (rich in both choline and omega-3s)
- Soybeans and legumes
- Wheat germ and bran
- Vegetables (though smaller amounts compared to animal sources)
Additionally, a Mediterranean-style diet, abundant in healthy fats, polyphenols, and antioxidant-rich foods, has been linked to improved cognitive performance, memory and executive function.9
Exercise
Regular aerobic and strength exercise supports acetylcholine production by:
- Increasing brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is directly involved in acetylcholine release and synapse maintenance.10
- Increasing the release of nitric oxide (NO), which works synergistically with acetylcholine to enhance vasodilation.11
Clinical Pearl: In older adults, low choline intake is associated with reduced gains in strength and muscle quality during resistance training, suggesting that adequate choline is important for muscle function and possibly acetylcholine-related neuromuscular activities.12
Mind-Body Practices
Mind-body practices can help promote increased focus, attention and cognitive performance; however, there isn't evidence to suggest a direct impact on acetylcholine production.
- Controlled breathing exercises, such as pranayama or diaphragmatic breathing, may help regulate cholinergic signaling, vagal tone and enhance parasympathetic nervous system activity, supporting cognitive clarity.13
- Mindfulness meditation has been shown to enhance attention processing and emotional regulation through improved brain connectivity and neuroplasticity.14,15
- Time in nature ("green therapy") may support acetylcholine balance by reducing stress hormones.16
Clinical Pearl: Engage in physical activity in nature for an extra win!
Electronic Detox
In the digital age, one of the most pervasive disruptors of focus and cognitive efficiency is the constant influx of notifications, multitasking and screen time. Research indicates that frequent digital interruptions can lead to attention fragmentation, reducing the brain's ability to engage in sustained, deep work.17
To mitigate these effects, healthcare professionals can recommend structured digital detox strategies, such as:
- Establishing technology-free blocks during the day
- Turning off notifications
- Using "do not disturb" settings during cognitively demanding tasks
- Implementing screen-free morning and evening routines
- Encouraging periods of boredom, creative play and real-world sensory engagement, such as connecting with others in real life, walking in nature or journaling.
Nutrient Solutions to Optimize Acetylcholine
Targeted nutrient supplementation offers an evidence-based approach to supporting acetylcholine levels and cognitive function.
Choline is a direct precursor to acetylcholine, which is involved in attention and cognitive performance. Supplemental and dietary intake is associated with healthy memory, attention and learning. Not all forms of choline may provide the same benefits.18‡ Research suggests GPC and CDP-choline (citicoline) are bioavailable forms that efficiently cross the blood-brain barrier and support acetylcholine synthesis.18 Cognizin®, a patented citicoline, increases choline and phospholipid composition in the brain.19 Studies in children, middle-aged adults and elderly adults indicate that it supports healthy cognition across a wide age range. In two studies, one involving adolescent boys and another involving middle-aged women, 250-500 mg Cognizin® citicoline offered statistically significant support for daily mental task performance.20,21
Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALC) is an ester of the trimethylated amino acid L-carnitine. It plays a dual role in supporting cognitive function: it facilitates acetyl-CoA uptake to enhance acetylcholine production and supports mitochondrial energy production in neurons. Clinical trials suggest that ALC supplementation promotes mental clarity, reduces brain fog and supports focus in individuals with cognitive fatigue.22
American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolius) has been shown to modulate acetylcholine release and thereby promote learning and working memory.23 Its active components, known as ginsenosides, also possess protective properties that moderate oxidative stress-induced changes to cholinergic signaling.24
Phosphatidylcholine: choline is a precursor to phosphatidylcholine, a key phospholipid found in cell membranes and serves as a reservoir for choline needed for acetylcholine synthesis.25
Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid critical for synaptic function and neuronal membrane integrity. Multiple studies indicate that supplementation helps support mental acuity, behavioral and cognitive parameters.26–28
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The long-chain omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA promote healthy cognition, support the release of neurotransmitters and help protect against oxidative stress. One systematic review concluded that omega-3 fatty acid intake (1-2 grams daily) promoted executive function, word and memory recall and cognitive performance.29
Pure Encapsulations Nutrient Solutions
Pure Encapsulations® provides uniquely formulated products made with high-quality, pure ingredients backed by verifiable science to complement your plan of care and support the health of your patients.‡
Rapid Mental Energy is a non-stimulant formula that combines two clinically studied extracts, Alpinia galagna(enXtra) and American ginseng (Cereboost®), to support alertness and sharpen working memory, without interfering with sleep.23,30–33‡
Suggested Use: Take 1 capsule, as needed, with or between meals. It can be used in combination with caffeine.
Phosphatidylcholine (sunflower) is a phospholipid-bound choline that supports cellular function, cognitive function and liver health. It acts as a precursor for phospholipids and acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter involved in attention, memory and neuromuscular function.‡
Suggested Use: Take 2 capsules daily, with a meal
CogniPhos contains a blend of clinically researched Cognizin® citicoline, acetyl-L-carnitine, SharpPS® phosphatidylserine and cofactors to promote daily cognitive performance and mental sharpness while supporting cellular energy and optimal neuronal function. 21,27‡
Suggested Use: Take 2 capsules, 1-2 times daily, with meals or as directed by a healthcare professional
O.N.E™ Omega provides 1,000 mg of triglyceride-form EPA/DHA produced through a unique solvent-free, supercritical, CO2-based extraction method to support a healthy inflammatory response.‡
Suggested Use: Take 1 capsule daily, with a meal
Conclusion
Acetylcholine is a key neurotransmitter involved in attention regulation, memory formation and cognitive flexibility. Clinicians can provide integrative solutions to support acetylcholine production, including a choline-rich diet, regular physical activity, stress management techniques and key nutrients such as choline, phosphatidylcholine, acetyl-L-carnitine and omega-3 fatty acids to support sharper focus and cognitive performance in their patients.
Resources
Cognitive Performance Protocol: Designed by our scientific and medical advisors to help you deliver the most effective care and support for your patient.
Drug-Nutrient Interaction Checker: Provides valuable information on potential interactions between your patients' prescriptions, over-the-counter medications and nutritional supplements.
PureInsight™: Our streamlined platform easily collects patient data and provides valuable recommendations to help achieve their health goals.
Virtual Dispensary: Our Pure Patient Direct program provides account holders FREE access to our virtual dispensary to help simplify patient sales and reduce in-office inventory.
You can also explore Pure Encapsulations® to find On-Demand Learning, Clinical Protocols and other resources developed with our medical and scientific advisors.
References
- National Institute of Mental Health. National Institute of Mental Health. Accessed March 26, 2025. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics
- Duffy B, Thain M. The Policy Institute. Published online February 2022.
- Tizabi Y, Getachew B, Tsytsarev V, et al. In: Acetylcholine - Recent Advances and New Perspectives; 2023. doi:10.5772/intechopen.112447
- Bekdash RA.Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3). doi:10.3390/ijms22031273
- Newman EL, Gupta K, Climer JR, et al. Front Behav Neurosci. 2012;(JUNE). doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2012.00024
- Dautan D, Huerta-Ocampo I, Gut NK, et al. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1). doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15514-3
- Ballinger EC, Ananth M, Talmage DA, Role LW. Neuron. 2016;91(6). doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2016.09.006
- Decker AL, Duncan K. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2020;32. doi:10.1016/j.cobeha.2020.01.013
- Fu J, Tan LJ, Lee JE, Shin S. Front Nutr. 2022;9. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.946361
- Wang Q, Cui C, Zhang N, et al. J Orthop Translat. 2024;46:91-102. doi:10.1016/j.jot.2024.03.007
- Kingwell BA. The FASEB Journal. 2000;14(12). doi:10.1096/fj.99-0896rev
- Lee CW, Lee T V., Galvan E, et al. Nutrients. 2023;15(18). doi:10.3390/nu15183874
- Herhaus B. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2024;160. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2023.106751
- Calderone A, Latella D, Impellizzeri F, et al. Biomedicines. 2024;12(11):2613. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12112613
- Prakash RS. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. 2021;36(7). doi:10.1093/arclin/acab053
- Shuda Q, Bougoulias ME, Kass R. Complement Ther Med. 2020;53. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102514
- Duke É, Montag C. Addictive Behaviors Reports. 2017;6. doi:10.1016/j.abrep.2017.07.002
- Kansakar U, Trimarco V, Mone P, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1148166
- Silveri MM, Dikan J, Ross AJ, et al. NMR Biomed. 2008;21(10). doi:10.1002/nbm.1281
- McGlade E, Locatelli A, Hardy J, et al. Food Nutr Sci. 2012;03(06). doi:10.4236/fns.2012.36103
- McGlade E, Agoston AM, DiMuzio J, et al. J Atten Disord. 2019;23(2). doi:10.1177/1087054715593633
- Pennisi M, Lanza G, Cantone M, et al. Nutrients. 2020;12(5). doi:10.3390/nu12051389
- Scholey A, Ossoukhova A, Owen L, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010;212(3). doi:10.1007/s00213-010-1964-y
- Zhu Y, Wang Z, Yu S, et al. Molecules. 2022;27(22):7824. doi:10.3390/molecules27227824
- Tan W, Zhang Q, Dong Z, et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2020 Dec 16;68(50):14884-14895. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06383.
- Hirayama S, Terasawa K, Rabeler R, et al. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics. 2014;27(SUPPL2). doi:10.1111/jhn.12090
- Kato-Kataoka A, Sakai M, Ebina R, et al. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010;47(3). doi:10.3164/jcbn.10-62
- Richter Y, Herzog Y, Lifshitz Y, et al. Clin Interv Aging. 2013;8. doi:10.2147/CIA.S40348
- Dighriri IM, Alsubaie AM, Hakami FM, et al. Cureus. Published online 2022. doi:10.7759/cureus.30091
- Shin K, Guo H, Cha Y, et al. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology. 2016;78. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2016.04.006
- Bell L, Whyte A, Duysburgh C, et al. Eur J Nutr. 2022;61(1). doi:10.1007/s00394-021-02654-5
- Ossoukhova A, Owen L, Savage K, et al. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2015;30(2). doi:10.1002/hup.2463
- Srivastava S, Mennemeier M, Pimple S. J Am Coll Nutr. 2017;36(8). doi:10.1080/07315724.2017.1342576
+Kim Ross is a paid consultant for Pure Encapsulations.